

Treatment goals in buckle fractures are for patient comfort and parental reassurance. Therefore, an ever-present high index of suspicion is required, particularly if any inconsistencies in the history, delayed presentation, multiple injuries of different ages, or if the mechanism of injury does not equate to the given fracture pattern. One must also be aware that although radiographs may show a buckle fracture if a clinical deformity exists, there may also be a plastic deformation that requires correction.įinally, with children, one must always be wary of non-accidental injury (NAI). Additionally, general principles for the assessment of any bruising, swelling, or bony tenderness around the site of injury may indicate a fracture. Like with every trauma case, one should ascertain if there are any other injuries and to make sure this is not a distracting injury to something more pressing.ĭuring the physical examination, inspection is key, and one must assess for any clinical deformities. As with any trauma history, the mechanism of injury is of utmost importance. The history and physical examination of these injuries are relatively simple. However, if there is a fracture with a cortical breach, it is termed a greenstick fracture if unicortical or a complete fracture if bicortical.īuckle fractures are incredibly common injuries that present to the emergency department, which are invariably always managed conservatively, and do not routinely require orthopedic input. The appearance on plain X-ray shows the fracture site as two outcroppings of bone, as though the long bone has collapsed or ‘buckled.’ The word "torus" is the Latin word "protuberance. In long bones, injuries without a cortical break either lead to plastic deformation through microfracture or to a ‘kink’ within the long bone, described as a ‘buckle’ or ‘torus’ fracture. With soft, malleable bone, and a thick protective periosteal covering, minor injuries can result in a spectrum of deformities with or without a cortical break.

Two of the major differences include the presence of the physeal growth plate and a thicker periosteum with the softer underlying bone. Treatment of radial head fractures depends on the specific characteristics of the fracture using the Mason classification.The pediatric skeletal anatomy has unique properties that lead to varied pathology to that of the adult skeleton. Radial head fractures may be difficult to visualize on initial imaging but should be suspected when there are limitations of elbow extension and supination following trauma. Combined fractures involving both the ulna and radius generally require surgical correction. These fractures are treated with immobilization or surgery, depending on the degree of displacement and angulation. Isolated midshaft ulna (nightstick) fractures are often caused by a direct blow to the forearm. It should be noted that these fractures may be complicated by a median nerve injury. A nondisplaced, or minimally displaced, distal radius fracture is initially treated with a sugar-tong splint, followed by a short-arm cast for a minimum of three weeks. In adults, distal radius fractures are the most common forearm fractures and are typically caused by a fall onto an outstretched hand. Depending on the degree of angulation, buckle and greenstick fractures can be managed with immobilization. Greenstick fractures, which have cortical disruption, are also common in children.
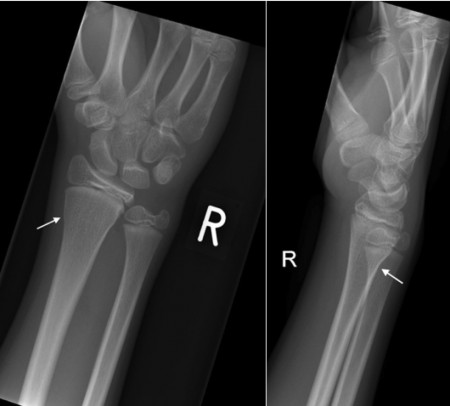
Incomplete compression fractures without cortical disruption, called buckle (torus) fractures, are common in children. If initial imaging findings are negative and suspicion of fracture remains, splinting and repeat radiography in seven to 14 days should be performed.
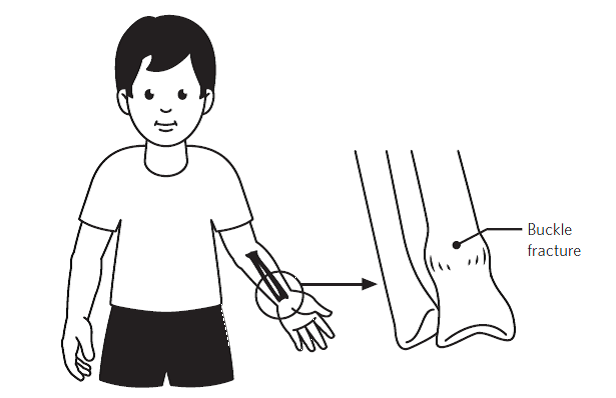
Evaluation with radiography or ultrasonography usually can confirm the diagnosis. A fall onto an outstretched hand is the most common mechanism of injury for fractures of the radius and ulna. Fractures of the radius and ulna are the most common fractures of the upper extremity, with distal fractures occurring more often than proximal fractures.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
